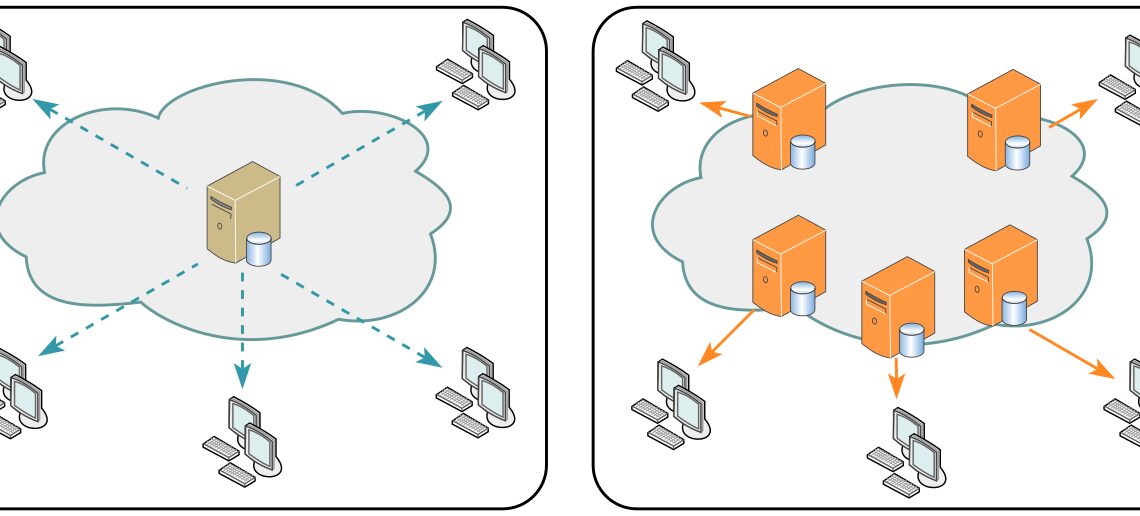
Web3 — the third generation of the internet — refers to a decentralized and distributed version of the web that uses blockchain technology, and other decentralized technologies, to enable greater user control, privacy and data ownership. It aims to redefine how we interact with digital services, moving from traditional centralized models to decentralized peer-to-peer networks.
At its core, Web3 is built on blockchain technology, which is a distributed ledger that maintains a cryptographically-secured, continuously growing list of records called blocks. This decentralized nature enables direct peer-to-peer interactions.
Web3 brings several key features and capabilities with the potential to revolutionize high-storage applications. Examples of high-storage applications include content delivery networks (CDNs) to host images and other visual media, online gaming platforms, and blockchain-based websites.
Unlike traditional centralized systems, Web3 ensures that no single entity has complete control or ownership over data. This decentralized approach makes the data resistant to censorship, manipulation, or single-point-of-failure risks, thereby enhancing data integrity and availability.
Harrison Hines, CEO and Co-founder of Fleek — a decentralized development platform — told Cointelegraph, “The well-designed protocols powering Web3 ensure decentralization through their network architecture, cryptography and token-economic incentive system.” He added:
“The benefits of this approach largely center around being trustless, permissionless, tamper-proof and censorship-resistant. These are increasingly important problems/issues, especially on corporate-owned Web2 cloud platforms, and Web3 does a great job addressing them.”
Ankur Banerjee, chief technology officer at Cheqd — a decentralized payments and identity platform — also weighed in, telling Cointelegraph, “Focusing specifically on decentralization, it provides resiliency away from single providers. There have historically been lots of outages due to cloud providers failing, e.g., only a week ago, Microsoft Outlook was down, and in January, Outlook, Teams, and 365 were all down, which shows the danger of centralization. Facebook’s global outage in 2021 took down not just their services, but large parts of the rest of the web which relied on Facebook’s ad tracking and log in.”
Another significant aspect of…
Click Here to Read the Full Original Article at Cointelegraph.com News…